Automated Accessibility Testing Made Simple
Accessibility has always been part of Drupal’s DNA but keeping it consistent across large sites takes more than good intentions. As standards evolve, developers and editors must balance WCAG compliance with design, content, and performance. This post looks at how automation and AI can make that work easier. From adding automated WCAG checks to CI pipelines to using AI tools that guide content editors, Drupal teams can spot problems earlier and fix them faster. At Cheppers, we’ve built a reliable, developer-friendly testing system for real Drupal projects, and we’re already preparing it for the next generation of WCAG guidelines.

Why Accessibility Still Falls Through the Cracks
A Drupal site can look modern and polished yet still miss the mark on accessibility. A missing label on a form, an image without an alt text description, or a navigation menu that can’t be used with a keyboard are small oversights that create real barriers for users. These issues don’t happen because teams don’t care. They happen because accessibility enters the process too late.
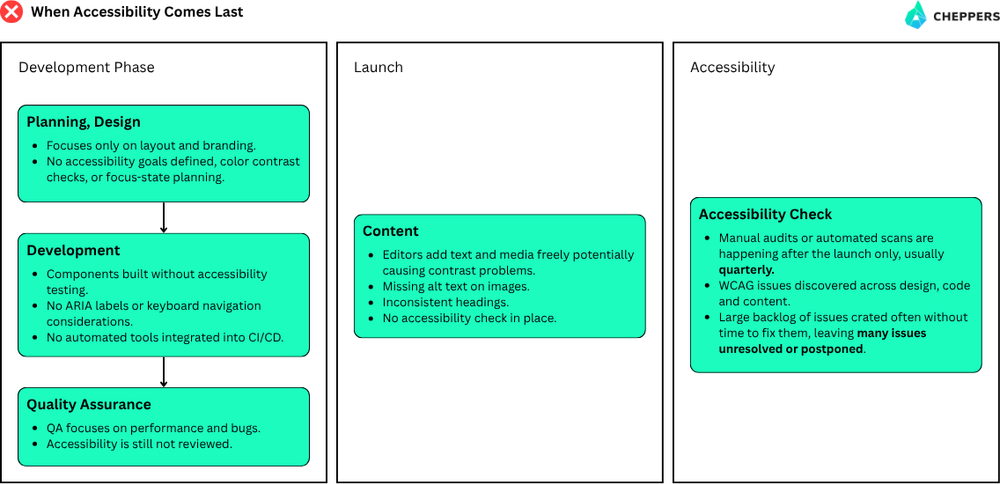
Many organizations check for accessibility only at the end of a project, when fixes are slow and expensive. Manual audits are valuable, but they’re difficult to repeat across large Drupal installations with frequent content changes. Automation helps fill that gap.
Tools like Pa11y, axe-core, and Lighthouse can test accessibility as part of development. They identify WCAG problems just like code quality or performance tools do. Adding them to CI/CD pipelines means each release is reviewed automatically. These checks don’t replace human expertise, but they provide a solid foundation that keeps accessibility visible and measurable from start to finish.
At Cheppers, we take the same approach. Accessibility should be part of everyday development, not a one-time milestone. Automated WCAG testing helps teams detect problems early, understand their causes, and address them continuously. Whether you use community tools or your own setup, the key is to make accessibility a routine part of how you work.

The Accessibility Challenge for Every Team
Accessibility is often associated with universities, NGOs, or public institutions, but it matters for every digital platform. Whether you manage an enterprise site, a local service, or an internal portal, accessible design shapes how people experience your brand and your message.
Across all these projects, the same challenges appear: content grows quickly, editors change, and design updates can reintroduce older issues. Automated testing gives teams a steady way to monitor quality without adding extra workload.
Artificial intelligence is now joining this effort. In Drupal, AI-driven tools can suggest alt text, highlight color contrast problems, and flag unclear headings or link text. When developers and editors use these tools together with automated WCAG checks, accessibility becomes a shared practice that blends into everyday work.
Built on Drupal’s Accessibility DNA
Drupal has long led by example when it comes to accessible web development. The Drupal Accessibility Team already follows WCAG 2.2 AA guidelines across core features and documentation. You can read more about this commitment on Drupal.org’s accessibility page. This leadership gives every Drupal project a strong foundation to build on.
But accessibility is never static. Each site, module, and design decision adds new layers that affect how users interact with the platform. As Drupal professionals, it’s our responsibility to keep pace with these standards and follow the same discipline the Drupal core team demonstrates.
Developers can run automated WCAG tests in their build pipelines to catch issues early. Editors can use AI-based tools that highlight missing alt text or structural problems before publishing. Designers can verify color contrast, font size, and interactive states to maintain readability and focus. When every contributor adopts this mindset, accessibility remains consistent from concept to launch and throughout the life of the site.
How Cheppers’ Automated WCAG Testing Works
At Cheppers, we created an internal accessibility testing system built and designed by Dávid Segesvári, one of our senior Drupal specialists. The system combines automation, clear reporting, and expert analysis to help Drupal teams maintain high standards over time.
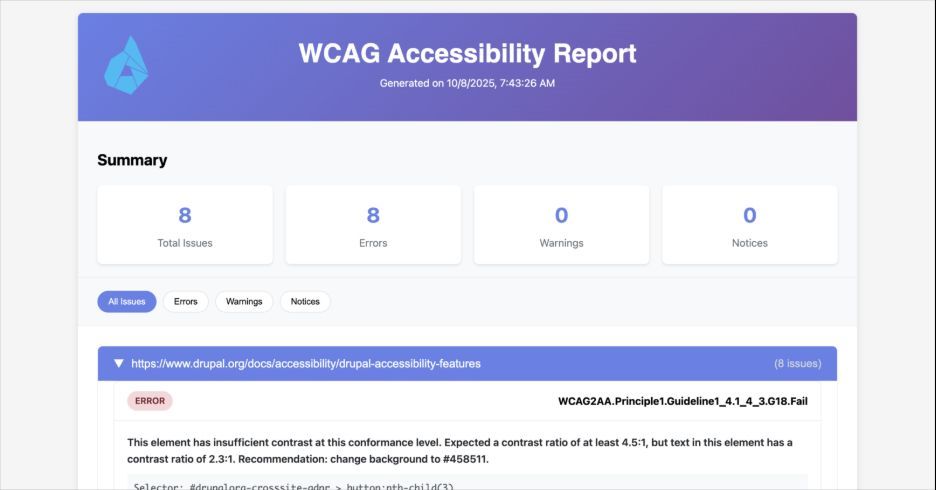
It scans templates, pages, and components, then compiles easy-to-read reports that explain what needs attention and why. Content editors can use these insights to improve accessibility directly on their pages, while the team receives scheduled email summaries that keep progress visible without extra effort.
Each project uses a slightly different setup. Some teams prefer scans on every deployment, while others choose regular audits that track long-term trends. Both methods lead to the same result: a clear view of how accessible your site truly is and a straightforward path to improving it.
If you’d like to explore how this testing process could support your Drupal workflow, contact our team. We’re always happy to hop on a call, or just chat and share details and examples.
Real Impact for Drupal Sites
Many long-running Drupal sites accumulate thousands of images, documents, and layout changes over the years. It’s easy for accessibility issues like missing alternative text, unclear heading levels, or outdated color contrast to slip through during regular updates. Automated WCAG testing can help uncover these patterns at scale.
Our current system already meets WCAG 2.1 AAA and follows WCAG 2.2 AA in audits and reports. WCAG 3.0 has no release date yet, but its draft introduces new ways to measure accessibility. We’re already weaving those ideas into our work so clients stay ahead.
By scanning the entire site, teams can quickly identify where problems cluster and fix them at their source, often improving hundreds of pages in one effort. Automation brings structure and visibility to a process that would otherwise rely on manual review. It helps teams focus on practical improvements that make content more usable for everyone.
Over time, this approach turns accessibility into a steady, ongoing rhythm instead of a reactive project. Each small correction adds up, creating sites that are both compliant and genuinely easier to navigate.
Accessibility Without Barriers
Accessibility improves the experience for everyone: students, donors, customers, and staff alike. Drupal already provides a strong foundation, but true accessibility grows through consistent habits, thoughtful collaboration, and the right tools.
Every team can begin by adding automated checks, reviewing content with accessibility in mind, and keeping inclusion part of everyday development. Small steps like these create lasting impact over time.
At Cheppers, we continue to refine and share the methods that make this process simpler for Drupal projects of all sizes. If your organization wants support in setting up automated WCAG testing or developing a long-term accessibility strategy, we’re always ready to help.
Related posts

Artificial intelligence has become one of the defining conversations of our time. Some see it as a revolutionary force with limitless potential, while others think it is a looming threat, raising concerns about control, jobs, and trust. For leaders, product teams, editors, and developers, the real question is simpler and more practical: how can AI help people focus on the work that matters while handling the repetitive tasks?

Search is no longer what it used to be. For many years the process was simple. People typed a question into Google, browsed the links that appeared, and clicked the result that looked most promising. Businesses, especially those running Drupal websites, built entire strategies around search engine optimization to capture those clicks and grow their audience.

